GPT4控制暖通空调
大模型 工业 看到一篇用GPT4控制暖通空调的论文。暖通空调(Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning, HVAC)是指室内或车内负责暖气、通风及空气调节的系统或相关设备。用LLM控制HVAC,听上去非常有趣,又是一个LLM在工业领域落地的案例。
方法
先来看控制流程图:
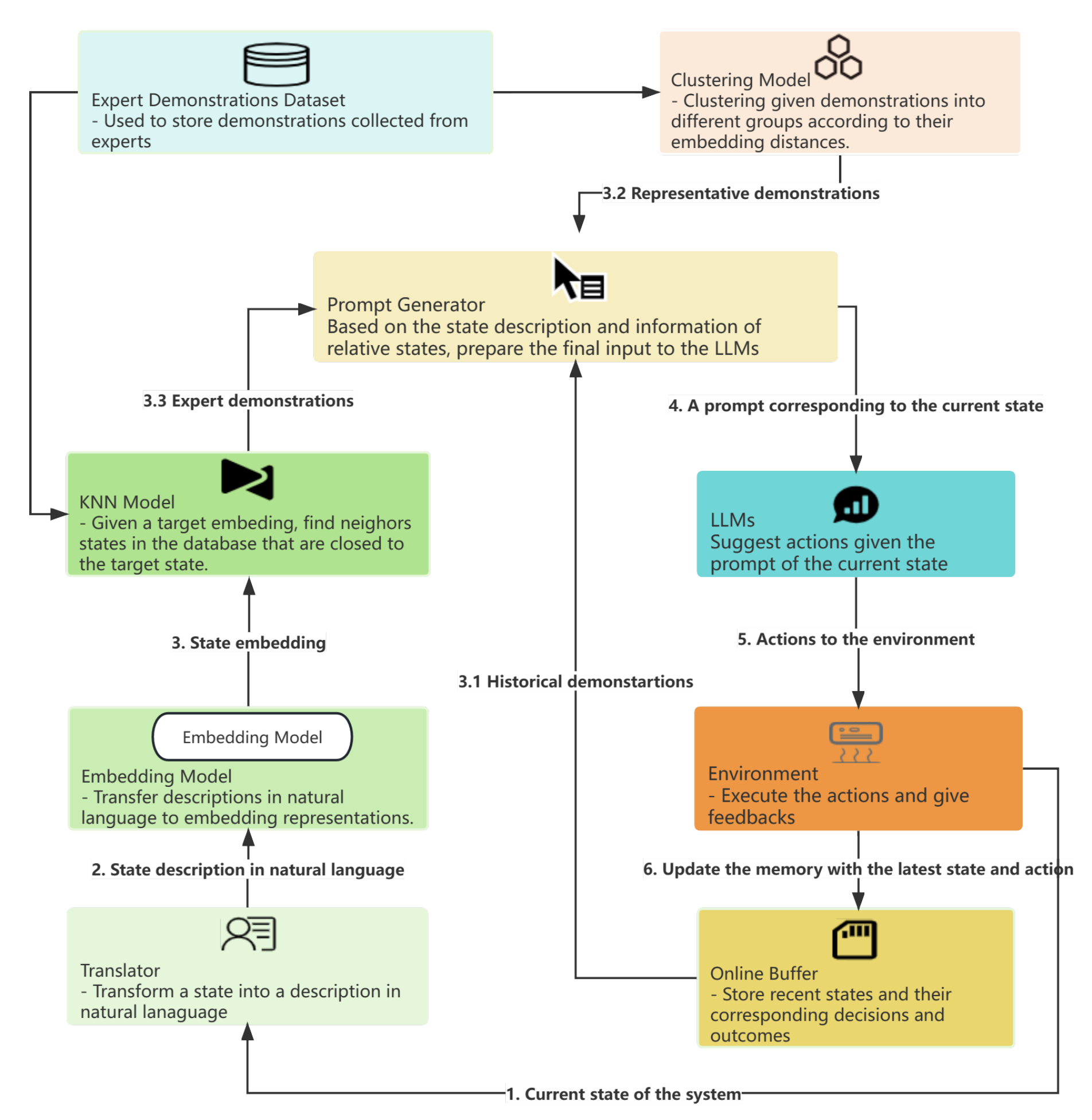
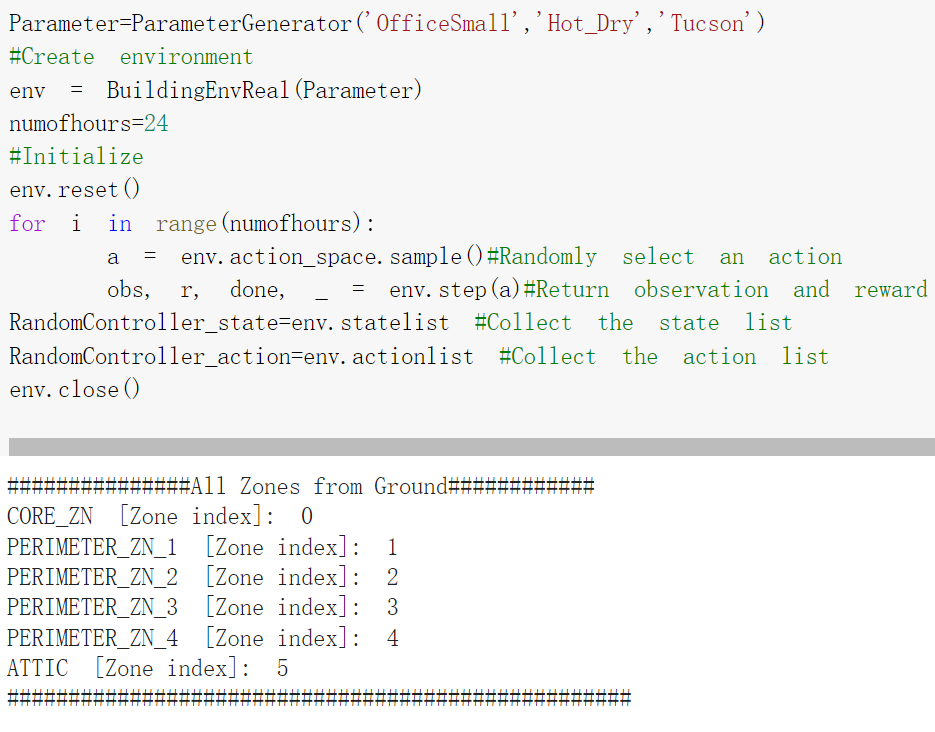
控制HVAC的过程类似强化学习:控制器与环境交互,从环境获取反馈,再根据反馈执行某个控制动作。论文用BEAR模拟建筑物环境。例如,要创建一个炎热干燥、位于图森(Tucson)的小型办公室环境,BEAR的代码如下:
BEAR用向量表示环境的状态:前面的每个维度都表示建筑物内一个房间的温度,最后4个维度分别表示室外温度、地面辐射强度、地温和入住房间耗电功率。控制HVAC的目标是尽量保持22摄氏度的室温(体感最舒适的温度),同时尽量减少电力消耗。
BEAR用[-1, 1]之间的数字表示动作:负数表示制冷模式,正数表示制热模式。绝对值越大,表示空调的阀门开度越大,从而能耗越高。
为了兼顾舒适性和低能耗,设计如下的奖励函数:
\[\left(1.0-\frac{\sum_{0\leq i<n}\lvert a_{i}\rvert}{n}\right) + \alpha \cdot \left(1.0-\frac{\sum_{0\leq i<n}(t_{i}-T)^2}{T\cdot n}\right)\]其中,n是房间数量,T=22是目标温度,\(t_{i}\)是第i个房间的温度。每当控制器做出一个动作,环境就返回一个奖励值。
有了以上的背景知识,根据上面的控制流程图,HVAC的控制流程可以描述如下:
- 把当前状态(包括状态向量、建筑类型、天气、城市等)输入翻译器,翻译成自然语言
- 把自然语言输入Universal Sentence Encoder,得到表示当前状态的嵌入向量,即目标向量
- 使用KNN算法,从专家示例数据库中找到若干距离目标向量最近的专家示例
- 使用K-means算法,对专家示例数据库聚类,得到若干代表性专家示例
- 从在线经验数组中获取最近几次交互历史
- 把当前状态、最近专家示例、代表性专家示例以及最近交互历史都输入提示词生成器,生成提示词
- 把提示词输入大模型,大模型输出要执行的动作
- 在BEAR创建的环境中执行动作,获得奖励反馈以及下一个状态,并把最新交互存入经验数组
循环执行以上8个步骤,就可以实现用大模型控制HVAC了。
那么,上面提到翻译器、专家示例数据库、在线经验数组等概念,又是什么呢?
- 翻译器(Translator):把状态翻译成自然语言,方便大模型处理。论文中用到的翻译器有下面几种:
- metaTranslator:把建筑类型、天气、城市等元数据翻译成自然语言,例如:
You are the HVAC administrator responsible for managing a building of type Office Medium located in Buffalo, where the climate is Hot and Dry.
- instructionTranslator:根据室外温度的不同,生成制热或制冷模式对应的指令。当室外温度低于目标温度时,生成制热指令,当室外温度高于目标温度时,生成制冷指令,例如,下面的指令对应制热模式:
Currently, outside temperature is lower than the target temperature.
To optimize HVAC control, adhere to the following guidelines:
1. Actions should be represented as a list, with each integer value ranging from 0 to 100.
2. The length of the actions list should correspond to the number of rooms arranged in the same order.
3. If room temperature is higher than the target temperature, the larger the difference between room temperature and the target temperature, the lower the action should be.
4. If room temperature is lower than the target temperature, the larger the difference between room temperature and the target temperature, the higher the action should be. - stateTranslator:把状态向量翻译成自然语言。大模型理解整数比理解浮点数更容易,因此输入翻译器之前,把向量各维度都做了取整运算。例如,一座建筑物有4个房间,温度分别是21, 20, 23和19摄氏,翻译器输出下面的指令:
The building has 4 rooms in total.
Currently, temperature in each room is as follows:
Room 1: 21 degrees Celsius
Room 2: 20 degrees Celsius
Room 3: 23 degrees Celsius
Room 4: 19 degrees Celsius
The external climate conditions are as follows:
Outside Temperature: -17 degrees Celsius.
Global Horizontal Irradiance: 0
Ground Temperature: 0 degrees Celsius
Occupant Power: 0 KW
Target Temperature: 22 degrees Celsius - actionTranslator:把动作从位于[-1, 1]的数字翻译成位于[-100, 100]的数字并取整。例如,一个动作序列是[0.95, 0.9, 0.72, 0.68], 翻译器输出:
Actions: [95, 90, 72, 68]
- feedbackTranslator:把执行专家示例的动作产生的输出(奖励和下一个状态)翻译成自然语言,和前面介绍的翻译器一样,把奖励和动作都转成整形,例如:
Reward: 8
Actions: [90, 92, 76, 97]
Comments: After taking the above actions, temperature in each room becomes:
Room 1: 23 degree Celsius
Room 2: 22 degree Celsius
Room 3: 20 degree Celsius
Room 4: 24 degree Celsius
The action for Room 1 shall be decreased as its temperature is higher than the target temperature.
The action for Room 3 shall be increased as its temperature is lower than the target temperature.
The action for Room 4 shall be decreased as its temperature is higher than the target temperature.
- metaTranslator:把建筑类型、天气、城市等元数据翻译成自然语言,例如:
- 专家示例数据库(Expert demonstrations Dataset):对BEAR提供的不同场景训练不同的PPO策略模型,每个模型训练1亿步,然后执行这些策略,每个策略执行100000步,收集20000个这样的轨迹,作为专家数据库。
- 在线经验数组(Online Buffer):存储最近大模型和环境交互的队列。
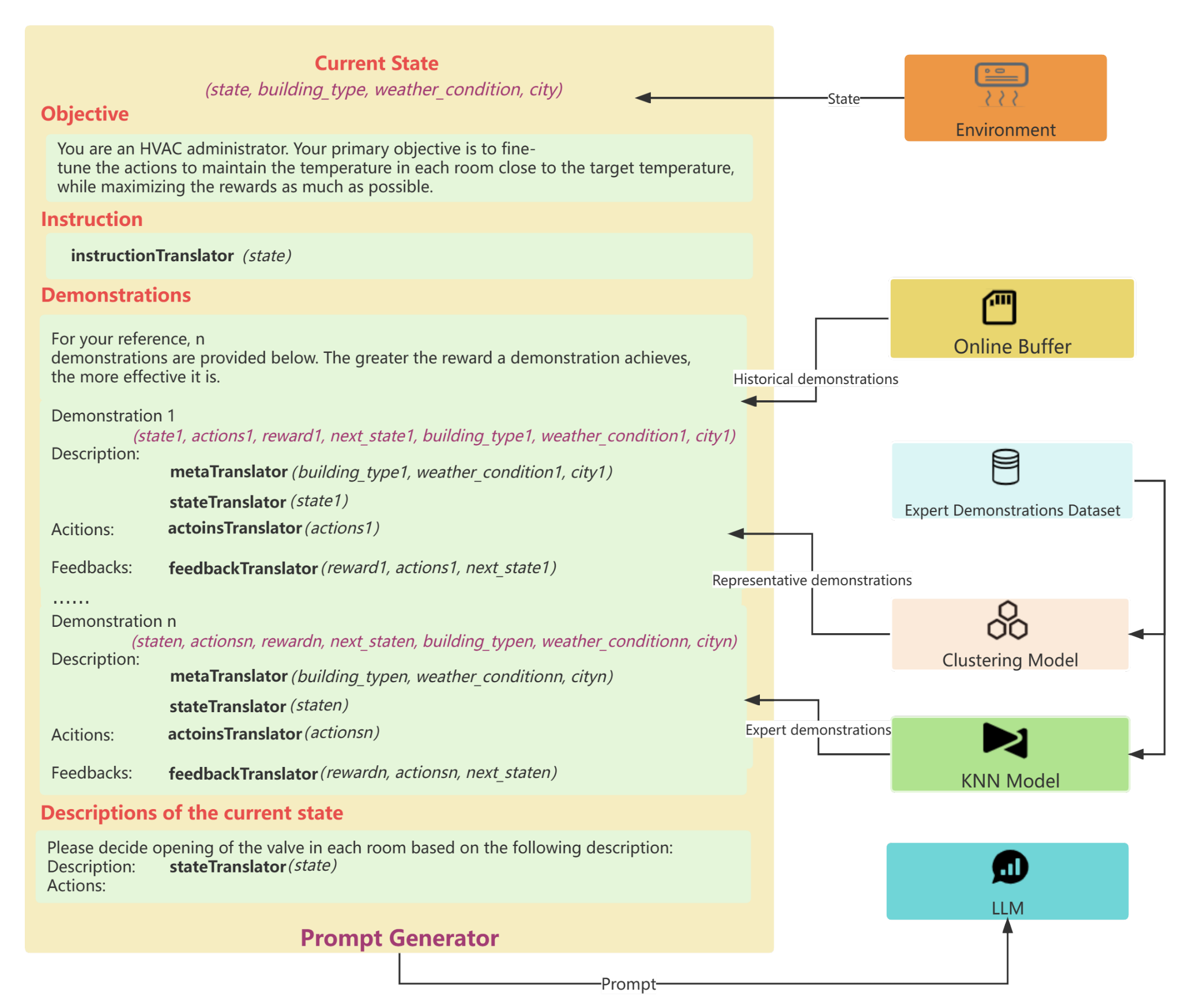
- 提示词生成器(Prompt Generator):综合当前状态、专家示例、在线经验等信息,生成提示词,如下图所示:
感悟
方法简单直观,但不代表没有价值。工业应用大模型的套路可能就是如此,先把各种向量和数值转化成自然语言,然后输入大模型,再把大模型的输出变回向量或数值,让控制器执行。终于不是文档问答那一套了!如果在控制过程中引入一些外部知识,例如文档,会不会效果更好呢?不知道,也可能把知识学杂了。